Coronary risk profile
Definition of Coronary risk profile
A coronary risk profile is a battery of blood tests to measure your cholesterol and triglyceride levels. The profile can help determine your risk for heart disease.
Alternative Names for Coronary risk profile
Lipoprotein/cholesterol analysis; Lipid profile; Lipid panel; Hyperlipidemia - testing
Normal Values
The ideal values are different for people without coronary artery disease or other risk factors than for those with known coronary artery disease, diabetes, or high blood pressure. The desired values in adults are:
- LDL: 70 - 130 mg/dL (lower numbers are desired)
- HDL: greater than 40 - 60 mg/dL (higher numbers are desired)
- Total cholesterol: less than 200 mg/dL (lower numbers are desired)
- Triglycerides: 10 - 150 mg/dL (lower numbers are desired)
- VLDL: 2 - 38 mg/dL
Talk to your health care provider about the ideal levels in children.
Note: mg/dL = milligrams per deciliter
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What abnormal results mean
Abnormal values may be a sign that you are at increased risk for atherosclerosis and related disorders, including:
- Heart disease
- Kidney disease
- Poor blood supply to the legs
- Stroke
What the risks are
Veins and arteries vary in size from one patient to another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling light-headed
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Cholesterol test
Definition of Cholesterol test
A total cholesterol test measures all the cholesterol in your blood.
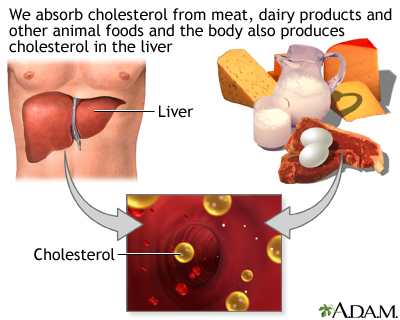
Cholesterol is a soft, wax-like substance found in all parts of the body. Your body needs a little bit of cholesterol to work properly. But too much cholesterol can clog your arteries and lead to heart disease.
Some cholesterol is considered "good" and some is considered "bad." Different blood tests are needed to individually measure each type of cholesterol.
Normal Values
Total cholesterol is an important measure of both bad and good cholesterol. Other lab tests are done to measure specific amounts of good (HDL) and bad (LDL) cholesterol. A cholesterol breakdown including LDL and HDL is preferred under certain circumstances.
The total cholesterol values listed below are used to target therapy:
- Desirable: Under 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
- Borderline high: 200 to 239 mg/dL
- High risk: 240 mg/dL and higher
What abnormal results mean
In general, a total cholesterol value over 200 mg/dL may mean you have a greater risk for heart disease. However, LDL levels are a better predictor of heart disease, and they determine how your high cholesterol should be treated
.Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like material that is found in all parts of the body. It comes from two sources: our liver produces it, and we consume it in meat and dairy products.
LDL test
Definition of LDL test
LDL stands for low-density lipoprotein. It's also sometimes called "bad" cholesterol. Lipoproteins are made of fat and protein. They carry cholesterol, triglycerides, and other fats, called lipids, in the blood to various parts of the body.
This article discusses the blood test to measure the level of LDL cholesterol in your blood. Too much LDL in the blood can clog arteries.
Normal Values
A healthy LDL level is one that falls in the optimal or near-optimal range.
- Optimal: Less than 100 mg/dL (less than 70 mg/dL for persons with a history of heart disease or those at very high risk for atherosclerotic disease)
- Near Optimal: 100 - 129 mg/dL
- Borderline High: 130 - 159 mg/dL
- High: 160 - 189 mg/dL
- Very High: 190 mg/dL and higher
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
High blood cholesterol and triglycerides
Definition of High blood cholesterol and triglycerides
The medical term for high blood cholesterol and triglycerides is lipid disorder. Such a disorder occurs when you have too many fatty substances in your blood. These substances include cholesterol and triglycerides.
Alternative Names for High blood cholesterol and triglycerides
Lipid disorders; Hyperlipoproteinemia; Hyperlipidemia; Dyslipidemia; Hypercholesterolemia
Treatment of High blood cholesterol and triglycerides
Treatment depends on your age, health history, if you smoke, and other risk factors for heart disease, such as:
- Diabetes
- Poorly controlled high blood pressure
- Family history of heart disease
The recommended values for adults are different depending on the above risk factors, but in general:
- LDL: 70-130 mg/dL (lower numbers are better)
- HDL: more than 40-60 mg/dL (high numbers are better)
- Total cholesterol: less than 200 mg/dL (lower numbers are better)
- Triglycerides: 10-150 mg/dL (lower numbers are better)
There are steps that everyone can take to improve their cholesterol levels, and help prevent heart disease and heart attack. Here are the most important ones:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet with plenty of fiber-rich fruits and vegetables. Avoid saturated fats (found mostly in animal products) and trans-fatty acids (found in fast foods and commercially baked products). Instead, choose unsaturated fats
- Exercise regularly to help raise your HDL ("good" cholesterol)
- Get periodic health checkups and cholesterol screenings
- Lose weight if you are overweight
- Quit smoking
If lifestyle changes do not change your cholesterol levels enough, your doctor may recommend medication. There are several types of drugs available to help lower blood cholesterol levels, and they work in different ways. Some are better at lowering LDL cholesterol, some are good at lowering triglycerides, while others help raise HDL cholesterol.
The most commonly used and most effective drugs for treating high LDL cholesterol are called statins. You doctor will choose one of these: lovastatin (Mevacor), pravastatin (Pravachol), simvastatin (Zocor), fluvastatin (Lescol), torvastatin (Lipitor), rosuvastatin (Crestor).
Other drugs that may be used include bile acid sequestering resins, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, fibrates, and nicotinic acid (niacin).
HDL test
Definition of HDL test
HDL stands for high-density lipoprotein. It's also sometimes called "good" cholesterol. Lipoproteins are made of fat and protein. They carry cholesterol, triglycerides, and other fats, called lipids, in the blood from other parts of your body to your liver.
This article discusses the blood test used to measure the level of HDL cholesterol in your blood.
Normal Values
In general, your risk for heart disease, including a heart attack, increases if your HDL cholesterol level is less than 40 mg/dL.
An HDL 60 mg/dL or above helps protect against heart disease.
Women tend to have higher HDL cholesterol than men.
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
C-reactive protein
Definition of C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein is produced by the liver. The level of CRP rises when there is inflammation throughout the body.
This article discusses the blood test done to measures the amount of CRP in your blood.
Alternative Names for C-reactive protein
CRP; High-sensitivity C-reactive protein; hs-CRP
Why the test is performed
The CRP test is a general test to check for inflammation in the body. It is not a specific test. That means, it can reveal that you have inflammation somewhere in your body, but it cannot pinpoint the exact location.
Your doctor may order this test to:
- Check for flare-ups of inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or vasculitis
- Determine if anti-inflammatory medicine is working to treat a disease or condition
However, a low CRP level does not always mean that there is no inflammation present. Levels of CRP may not be increased in people with rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. The reason for this is unknown.
A more sensitive CRP test, called a high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) assay, is available to determine a person's risk for heart disease. Many consider a high CRP level to be a risk factor for heart disease. However, it is not known whether CRP is merely a sign of cardiovascular disease or if it actually plays a role in causing heart problems.
Normal Values
Normal CRP values vary from lab to lab. Generally, there is no CRP detectable in the blood.
Your doctor may also use a highly sensitive test called hs-CRP to help determine your risk of heart disease. According to the American Heart Association:
- You are at low risk of developing cardiovascular disease if your hs-CRP level is lower than 1.0mg/L
- You are at average risk of developing cardiovascular disease if your levels are between 1.0 and 3.0 mg/L
- You are at high risk for cardiovascular disease if your hs-CRP level is higher than 3.0 mg/L
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What abnormal results mean
A positive test means you have inflammation in the body. This may be due to a variety of different conditions, including:
- Cancer
- Connective tissue disease
- Heart attack
- Infection
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Lupus
- Pneumococcal pneumonia
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatic fever
- Tuberculosis
This list is not all inclusive.
Note: Positive CRP results also occur during the last half of pregnancy or with the use of birth control pills (oral contraceptives).
What the risks are
There is very little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one patient to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling light-headed
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Feel Free To Leave Comments To My Posts,Its Always Nice To Get Feed Back!:)
No comments:
Post a Comment