Definition of Teething
Teething is the growth of teeth through the gums in the mouth of infants and young children.
Alternative Names for Teething
Information
Teething usually begins when a baby is between 6 and 8 months old. All 20 baby teeth should be in place by the time a child is 30 months old. Some children do not show any teeth until much later than 8 months, but this is usually normal.
The two bottom front teeth (lower incisors) usually come in first.Next to grow in are usually the two top front teeth (upper incisors).
Then the other incisors, lower and upper molars, canines, and finally the upper and lower lateral molars come in.
The signs of teething are:
Acting cranky or irritableBiting or chewing on hard objects
Drooling, which may often begin before teething starts
Gum swelling and tenderness
Refusing food
Sleeping problems
Teething does NOT cause fever or diarrhea. If your child develops a fever or diarrhea and you are worried about it, talk to your health care provider.
Tips to ease your child's teething discomfort:
Wipe your baby's face with a cloth to remove the drool and prevent a rash.Give your infant a cool object to chew on, such as a firm rubber teething ring or a cold apple. Avoid liquid-filled teething rings, or any plastic objects that might break.
Gently rub the gums with a cool, wet washcloth, or (until the teeth are right near the surface) a clean finger. You may place the wet washcloth in the freezer first, but wash it before using it again.
Feed your child cool, soft foods such as applesauce or yogurt (if your baby is eating solids).
Use a bottle, if it seems to help, but only fill it with water. Formula, milk, or juice can all cause tooth decay.
You can buy the following medications and remedies at the drug store:
Acetaminophen (Tylenol and others) or ibuprofen can help when your baby is very cranky or uncomfortable.Teething gels and preparations rubbed right on your baby's gums may help the pain for a short while. Be careful not to use too much.
What not to do:
DO NOT tie a teething ring or any other object around your child's neck.DO NOT place anything frozen against your child's gums.
NEVER cut the gums to help a tooth grow in, because this can lead to infection.NEVER give your child aspirin or place it against the gums or teeth.
DO NOT rub alcohol on your baby's gums.
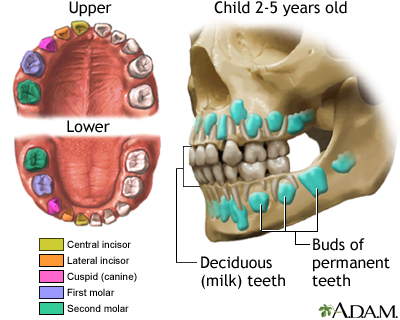
Development of baby teeth
Both baby teeth (deciduous or milk teeth) and permanent teeth have fairly well-defined times of eruption. The ages listed are the normal ages that a baby tooth emerges.
| UPPER | ERUPTS BY | LOWER | ERUPTS BY | |
| Central incisor | 8-10 Mo | Central incisor | 6-9 Mo | |
| Lateral incisor | 8-10 Mo | Lateral incisor | 15-21 Mo | |
| Canine (Cuspid) | 16-20 Mo | Canine (Cuspid) | 15-21 Mo | |
| First molar | 15-21 Mo | First molar | 15-21 Mo | |
| Second molar | 20-24 Mo | Second molar | 20-24 Mo |
Teething symptoms
Children typically begin to erupt a tooth between the 6th and 8th month of life. Signs of teething are: drooling, irritability, gum swelling and sensitivity, sleeping problems, refusing food, the urge to bite on hard objects and possibly a low grade fever. The discomfort that results from teething is due to the pressure exerted on the tissue in the mouth, called the periodontal membrane, as the teeth erupt.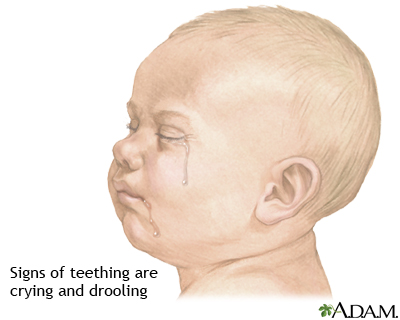

Feel Free To Leave Comments To My Posts,Its Always Nice To Get Feed Back!:)
No comments:
Post a Comment